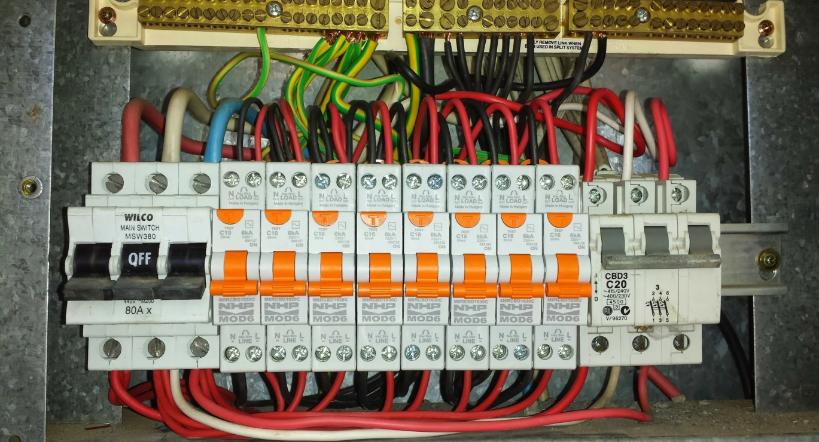
An electrical fuse box is a device that contains and handles fuses designed to protect an electrical system from overloading. It works as a central hub where electricity from the utility company is sent out to different circuits throughout a property. Nowadays electrical fuse boxes are referred to as switchboards.
Seeing how important its role is, regular checks and maintenance of an electrical fuse box or switchboard are crucial to ensure electrical efficiency and safety.
For this post, we’ll expand more on the role of an electrical fuse box and its main components.
What is the Role of an Electrical Fuse Box?
The role of an electrical fuse box is to keep an electrical system safe by stopping overcurrent, which can easily result in fires or damages. It does this by using fuses to interrupt the power flow when detecting an excessive current.
Besides its main function, electrical fuse boxes also play a key role in managing the electrical management of a building. These include the following responsibilities:
- Electricity distribution: The electrical fuse box distributes electricity from the primary power supply to different circuits within a building.
- Circuit segmentation: Every fuse in the electrical box is connected to a different circuit, allowing it to cater to different areas or appliances. Such segmentation allows for targeted protection that ensures only the circuit experiencing an overload is affected.
- Safety assurance: The electrical fuse box is designed to interrupt power during overloads to prevent electrical hazards.
- Troubleshooting and maintenance: The fuse box layout helps electricians quickly identify and resolve issues for each circuit.
- Operational continuity: When a circuit overload occurs, unaffected circuits will remain operational to ensure power supply continuity even to other areas in a building.
It’s safe to say that an electrical fuse box isn’t just a safety device but also a vital component to efficiently and effectively manage a building’s electrical infrastructure.
3 Main Parts of a Fuse Box
The 3 main parts of a fuse box or switchboard are the switchboard housing, main switch, and circuit breakers. Let’s take a closer look at each one below.
Switchboard Housing
The switchboard housing serves as the central hub for electrical distribution in your home. It safely directs electricity from the main supply to various circuits. Encased in a metal cabinet, this unit ensures effective management and protection of your electrical system.
Main Switch
The main switch is crucial, acting as the master control for your home’s electricity supply. It allows you to completely shut off the electrical supply, providing a safe way to manage power during maintenance or emergencies.

Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers play a key role in protecting your home from electrical overloads and short circuits. Each breaker is connected to a specific circuit. In the event of a fault or overload, the affected breaker automatically cuts off the power, thereby preventing damage and ensuring safety.
How Will I Know If I Need a New Fuse Box?
You will know if you need a new fuse box when signs such as tripping circuit breakers, an absence of RCDs, and regular fuse blowouts happen.
Other signs that you need a new fuse box are when it’s outdated, shows signs of overheating or damage, or inability to support current electrical demands.
Is a Fuse Box and a Switchboard the Same?
No, a fuse box and a switchboard aren’t the same. A fuse box mainly uses fuses for circuit protection, while a switchboard comes with RCDs and circuit breakers.
Both parts are crucial in managing and protecting a property’s electrical system, albeit using different technologies.